Gold monetization scheme (GMS) is announced by Finance Minister Arun Jaitley in the Union Budget 2015-2016. Now the Government has release the Draft guidelines for implementing this gold monetisation scheme.
According to the government, gold deposit accounts will utilise the 20,000 tonnes available within the country and help in cutting down the 800-1,000 tonnes of gold the country ships every year.
What is Gold monetisation scheme?
In simple terms, it is a scheme that allows people to deposit the gold / jewellery and earn Interest on their Gold Account.
A. Key Features of Gold monetization scheme
TAX FREE: Gold Monetization Scheme is proposed to be tax-free
- No Income tax on the Interest earned on Gold Account
- No Capital Gains Tax on the appreciation in the value of deposited gold
- No Wealth tax.
Interest: Interest rate will be decided by bank.
- Consumers will be paid interest on their gold savings account after 30/60 days of account opening.
- Interest will be credited in Gold. For e.g. If you deposit 100 gram gold and Interest rate is 1%, then 1 gram gold is credited to your account as Interest.
- The 1999 scheme offered an interest rate of 0.75-1% and flopped. Typically, the gold leasing rate is around 3-5%. Assuming that banks want a margin of 1-2%, the interest on gold deposits is likely to be only around 1-1.5% on the lower side.
Tenure: The tenure of gold deposits is likely to be for a minimum of one year and in multiples of one year. Pre mature breaking may be allowed (like Bank FD)
Minimum Deposit: The minimum quantity of deposits is kept at 30 gram to encourage even small deposits. It is different from the earlier SBI Gold Deposit scheme (1999) where minimum requirement is 500 grams.
Maturity / Redemption: The customer will have to choose an option of redemption either in cash or in gold. This option needs to be mentioned at time of making the deposit.
Where to deposit: Gold Monetization Scheme will initially be launched at few locations only because the government will have to first set-up infrastructure for facilitating easy and secure handling of gold.
B. Process for depositing gold in this scheme
- The customer needs to visit the any of the 350 Hallmarking Centers that are certified by Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). The centre will test the purity and provide estimated value of gold. If the customer agrees, he needs to submit the Bank KYC for and give his consent for melting gold. This process would take approx 1 hour.
- Gold will then be melted and its purity will be ascertained, If you are giving gold jewellery, gems or stones present in the jewelry will be handed-back to the customer. Only the gold will be taken. The time taken is expected not to exceed 3-4 hours.
- Based on the results, customer will have a choice to deposit the gold or take the melted gold after paying the nominal fees. If the customer agrees to deposit the gold, then he will be given a certificate by the collection centre certifying the amount and purity of the deposited gold.
- Customer will then visit the bank to open a Gold Savings Account. When the customer produces the certificate of gold depositd at the Purity Testing Centre, the bank will in turn open a Gold Savings Account for the customer and credit the ‘quantity’ of gold into the customer’s account. Simultaneously, the Purity Verification Centre will also inform the bank about the deposit made.
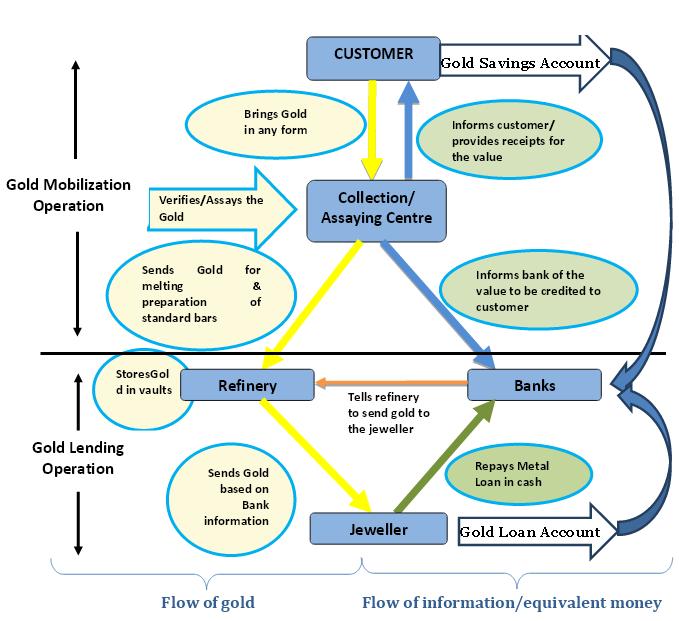
Flow diagram provided in the Gold Monetization Draft guidelines:
C. Benefits of Gold monetisation scheme to the Government and Banks
India is one of the world’s largest consumers of gold, importing as much as 800-1,000 tonnes every year, forcing the government to levy high import duties and putting other restrictions on gold imports. Gold is the second-biggest expense after oil on India’s import bill.
Banks will be allowed to use these deposits to meet their requirements for statutory liquidity ratio (SLR) and cash reserve ratio (CRR) requirements. SLR is the proportion of deposits that banks must invest in government securities and CRR is the proportion of deposits they must hold with the central bank.
Banks will also be permitted to sell the gold to generate forex reserves, which can be used by them for lending to exporters and importers. They can also trade on commodity exchanges or sell the gold to jewellers.
4. Feedback: The above draft rules are open for public feedback till 2nd June. You can check the link at https://mygov.in/group-issue/share-your-views-draft-gold-monetization-scheme/